Hard Operatİons
A huge ovarian cyst during pregnancy. This cyst was removed right before getting the baby out after a cesarean section.
So generally speaking, cysts might be discovered on an ultrasound, but do they pose any risks? That depend only on the size and the types of the ovarian cyst.
The major risk is of the pressure exerted by a large cyst on the womb. It can be prevented by carefully monitoring a woman, or by recognizing any signs of major problems early enough.
Most of the ovarian cysts are harmless (benign) and usually reduce on their own, but large cysts can cause problems and abdominal discomfort for a woman.
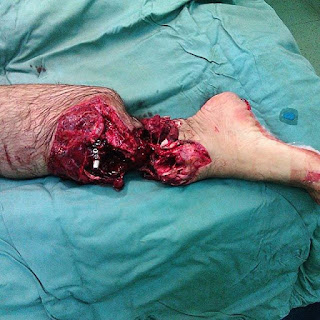
Reattachment (replantation) of an amputated part of the hand back to its place!
Replantation is the surgical reattachment of a body part, most commonly a finger, hand or arm, that has been completely cut from a person's body.
With the repair of the nerves and vessels (artery & vein) of the amputated part it is possible to restore the function and survival of the replanted part. Nowadays, Technological advances and the use of the microscope have made possible the replantation of parts including thumbs, fingers, ears, scalps, facial parts, and genitalia.
Carotid Body Tumour!
This curved reformat of a CT angiogram shows an arterial-phase enhancing lesion located between the internal and external carotid arteries. This is a typical location and appearance of a carotid body tumour (also known as carotid body paraganglioma). It is a highly vascular glomus tumour that arises from the paraganglion cells of the carotid body. Carotid body tumours are the most common type of paraganglioma of the head & neck, with the most common location being the carotid bifurcation.
Malignant features may be seen in 6% of head & neck paragangliomas.
Surgical excision is the treatment of choice. The larger the tumour the higher the risk of operative complications, which may require radiotherapy.
A fresh face transplant anyone? [EDUCATIONAL PURPOSE ONLY]. Face transplant is a medical procedure to replace all or part of a person's face.
It consists of a series of operations requiring rotating teams of specialists.
People with faces disfigured by trauma, burns, disease, or birth defects are main candidates for the procedure, with the main issue being the submission of otherwise physically healthy people to potentially fatal, lifelong immunosuppressant therapy. There are a lot of factors to consider when looking for an appropriate face transplant donor, issues of tissue type, age, sex, skin color, and consent from the donor's family. The patient's face is removed and replaced (sometimes including the underlying fat, nerves, blood vessels, bones, and/or musculature). The surgery may last anywhere from 8 to 36 hours, followed by a long period of recovery.
What a great way to start a new year, first moment a mother sees her twin boys, taken by @dralarcon and his colleagues.
Luck wasn't on this patient's side. A case of a broken femoral prosthesis of a 56 years old man following total hip replacement, who according to the clinical history was broken because of a fall.
To prevent such accidents, It is suggested that patients in the younger age group following total hip replacement should not expect to be able to lift excessively heavy weights, or to jump from any height.
Back to business! Polycystic kidneys vs. normal kidney (in the center). In Polycystic kidney disease, clusters of fluid-filled sacs, called cysts, develop in the kidneys and interfere with their ability to filter waste products from the blood. The growth of cysts causes the kidneys to become enlarged and can lead to kidney failure.
The disease frequently affect the kidneys, although patients may develop cysts in other organs such as liver, pancreas, ovaries and spleen.
Furthermore, it may even affect the heart or brain. If it affects the patient’s brain, it can hence lead aneurysm. If affects his heart, then the valves may become floppy leading heart murmur.
Frequent complications are dangerously high blood pressure (hypertension), pain in the back or sides, blood in the urine (hematuria), recurrent urinary tract infections, kidney stones, and heart valve abnormalities.
A non-invasive, reliable and inexpensive diagnosis is made by ultrasound.
Mandibular swing procedure for surgical resection of carcinoma of the oropharynx.
Mandibular “swing” appears to offer more versatility and fewer problems than either median labiomandibular glossotomy or lateral mandibulotomy. Good local control can be anticipated in properly selected patients because the tumor exposure is comparable to that achieved in operations involving jaw resection. It is a safe and effective approach in the surgical resection of the advanced oropharyngeal carcinoma, which can provide a good exposure for the oropharynx, supraglottic region, hypopharynx, the parapharyngeal space and the base of the skull.









Yorumlar
Yorum Gönder