New Operation
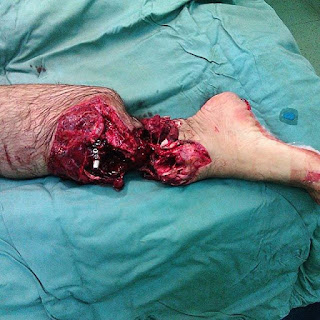
Peripheral giant-cell granuloma is what we call to this crazy oral pathology.
This condition represents the most common oral giant cell lesion, usually presents as a soft tissue purpulish-red nodule and microscopically consisting of a large number of multinucleated giant cells.
The etiology is still unknown, although there are assumptions that it can be stimulated by local irritation and trauma of the maxillary or mandibular gingiva (where is starts from in most cases). This lesion isn't considered as a true neoplasm, and it's usually not as large as in this case but has a relatively rapid growth rate, meaning that it can get pretty big if not removed surgically on time.
There you go! Surgical resection of the retro-orbital melanoma metastases in the patient that was discussed previously!
Fortunately, the operation went fine and the patient was discharged shortly afterwards.
Metastatic melanomas to the eye and orbit are rare and generally occur in patients with disseminated metastases during the terminal stages of the disease. Among the various treatment options, proton beam and global photon beam radiotherapies, at relatively high irradiation doses are effective as well.
Heart transplant in process! This doctor holds in his hands a diseased heart which had just been removed from a patient during a heart transplant operation. Cardiopulmonary (or heart-lung) bypass machine temporarily takes over the function of the heart and lungs during surgery, maintaining the circulation of blood and the oxygen content of the body. This patient is one step closer to get his new heart!
Meet your new best friend! (or enemy?). This is a typical bull's-eye rash (or erythema migrans) caused by Lyme disease.
Lyme disease, of course, is real. We all know to beware of ticks when we are walking in the woods, and to watch out for the bull’s eye rash around a bite that means Lyme disease. The disease is caused by a bacterium called Borellia burgdorferi that ticks carry and spread by their bites.
It can affect multiple organs like skin, joints (inflammatory arthritis), heart (myocarditis, pericarditis and heart block), and nervous system (limb numbness and pain, and paralysis of facial muscles). The first symptom is the bull's eye rash seen in the image above, and as the infection spreads patients might develop a chronic infection and have fever, headache, muscle and joint pain and fatigue. Some cases are hard to diagnose as the doctor may not have noticed a tick bite and 20-30% of patients doesn't develop any rash at all. Also, many of the symptoms are too general and resemble flu or other conditions.
Once diagnosed, antibiotics are pretty effective, and afterwards all is fine. Most people require a 2-4 week course, depending on the stage of the disease. In severe cases intravenous antibiotics can be administered.
Dental implant placement in a fresh extraction socket.
The term "fresh socket" refers to the period immediately after tooth extraction.
Dental implants can be placed in sockets just after tooth extraction (immediate implants) or after a couple of weeks up to a couple of months (immediate‐delayed implants) or thereafter (delayed implants). Implant placement has challenges in implant dentistry because tooth loss lead to bone resorption and collapse of gingival architecture, which lead to aesthetic compromise and inadequate bone for implant placement. Considering these, Immediate implant placement into fresh extraction socket reduces the treatment time, cost, preserves the gingival aesthetic and increases the comfort of the patient. Although there is a debate upon which is the best time to place dental implants, the aesthetic outcome could be better when placing implants early after tooth extraction, though early placed implants might be at a higher risk of failure.
Enucleation surgery (removal of the eye) in a patient with retinoblastoma!
Retinoblastoma is a rare malignant tumor of the retina, affecting young children, typically before the age of 5. Surgery is not needed for all retinoblastomas, especially for smaller tumors. But if a tumor gets quite large before it is found, vision in the eye has often already been destroyed, with no hope of getting it back. The usual treatment in this case is enucleation, an operation to remove the whole eye, plus part of the optic nerve attached to it. This is done while the patient is under general anesthesia (in a deep sleep).
During the same operation, an orbital implant is usually put in to take the place of the eyeball. The implant is made out of silicone or hydroxyapatite (a substance similar to bone). It is attached to the muscles that moved the eye, so it should move the same way as the eye would have.
Now that's a healthy heart, the perfect transplant for a patient in need! Do you heart this heart?
A postoperative photo of the same finger following a reconstructive surgery. In some cases the replantation of the fingertip is doubtful as for the outcome, but this one had a good functional outcomes! Happy ending
One of the things you get to see in the emergency department. The fingertip got literally chopped off!
fingertip injuries are very common in accidents at home, work, and play. They can occur when a fingertip slams in a car door, or while chopping vegetables, or in any activity that sounds unharmful.
Fingertips are rich with nerves and are extremely sensitive. Without prompt and proper care, a fingertip injury can disrupt the complex function of the hand, possibly resulting in permanent deformity and disability.
Snapped in the ER by @aws_al
Skillful surgeons remove a tumor from a woman's brain.
Malignant tumors indicate often lethal brain conditions, but even nonmalignant growths can preempt normal brain activity. Any tumor may compress regions of the brain and increase internal pressure, upsetting the organ's delicate functional balance. This is when neurosurgery come into play. Surgery is the initial treatment for most benign and many malignant tumors. It's worth noting that these kind of procedures are performed on patient who are either asleep or heavily sedated. In addition, the brain does not “feel” pain, and all of the surrounding tissues (eg, the scalp) are numbed prior to surgery.
This photo shows the recurrent laryngeal nerve (center) in a total thyroidectomy surgery.
This nerve innervates all the intrinsic muscles of the larynx with the exception of the cricothyroid muscle, which is innervated by the superior laryngeal nerve.
One common complication during a thyroid surgery is an injury to the recurrent laryngeal nerve, resulting in the vocal cord paresis or paralysis due to the damage of the posterior cricoarytenoid muscles, the only muscles that can open the vocal cords and are innervated by this nerve, eventually causing difficulties in breathing (dyspnea) during physical activity, as well as weakened voice (hoarseness) or loss of voice (aphonia) and problems of the respiratory tract due to the loss of a proper muscle function.
That's why this nerve receives close attention from surgeons since during thyroid or parathyroid surgery the nerve is at risk for injury.
A typical picture of GIST (Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor) from a patient that went through a subtotal gastrectomy.
GISTs are pretty common mesenchymal neoplasms of the GI tract. They are tumors of the connective tissue, which means that they are non-epithelial in origin, and are associated with several genetic mutations such as c-KIT mutations in more than 80% of the cases. The patient might have GI bleeding, trouble swallowing, intestinal obstruction and metastases to the adjacent organs (mainly to the liver). Surgical resection is the primary treatment of choice when a resectable GIST is present, although medications can be useful as well.
Surgical excision of a liver tumor. Hepatoblastoma is a rare cancerous tumor of the the liver that mainly affects children and does not spread outside of the liver, but rare cases of metastasis do occur, with the lung being the predominant site of metastases both at presentation and relapse. The etiology is unknown, although some genetic conditions has been associated with an increased risk for developing hepatoblastoma, including Beckwith-Weidemann syndrome, familial adenomatosis polypi, Wilson disease and other conditions like low birth weight and inborn errors of metabolism as are the glycogen storage diseases. Symptoms can vary depending on the size and location of the tumor and whether or not metastasis occurred. These are swollen abdomen, fever, weight loss, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and jaundice. The primary treatment is surgical resection, however, chemotherapy plays an important role by increasing the number of tumors that are resectable. The prognosis for patients with resectable tumors is fairly good, however, the outcome for those with nonresectable or recurrent disease is poor.














Yorumlar
Yorum Gönder